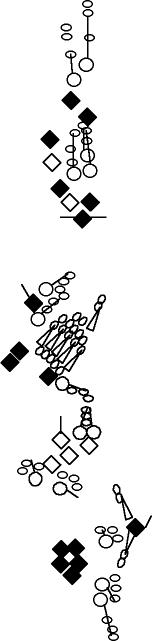
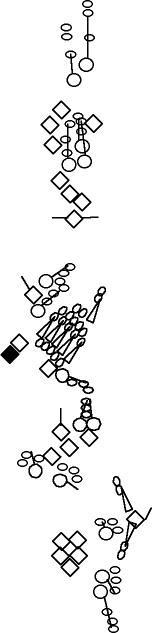
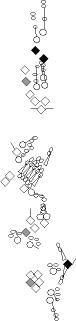
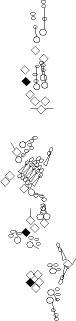
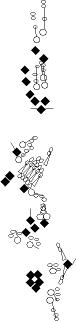
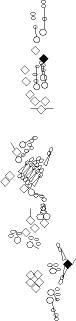
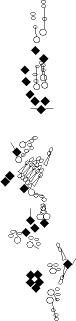
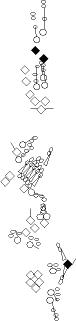
PNS expression patterns (3)
Gal4 lines
Expression
pattern in the embryonic
PNS at stage 15-17 is schematized here. Black cells are cells that
accumulate high levels of the marker, whereas grey cells accumulate low
levels and white cells do not accumulate the marker. Cells for which the expression has not been studied are represented by a light grey line. Expression pattern at earlier embryonic stages is also mentioned in the text below each diagram.
Click on a marker name to link to
the
corresponding FlyBase page.
|
|
C161-GAL4
|
|
c929-gal4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expression is not detected in embryonic stages (Shepherd and Smith, 1996). In the larva, C161-GAL4 is strongly expressed in five dorsal
multidendritic neurons (Shepherd and Smith, 1996): ddaA, ddaB, ddaD, ddaE and ddaF (Williams and
Truman, 20005). In the ventral and lateral regions,
C161-GAL4 is expressed in vdaA, vdaB, vdaC, vdaD, vbd, vpda, lbd, ltd,
ldaA, ldaB and in a scolopale of a lateral chordotonal organ (Shepherd and Smith, 1996). This P-element is inserted into the smallminded gene (Long et al., 1998).
|
|
Expression is detected in the lbd neuron (Hewes et al., 2003). This P element is inserted in the dimmed gene (Hewes et al., 2003).
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gal4221
|
|
Gal4477
|
|
Gal4109(2)80
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| It accumulates at a high level in the class I md neurons (vpda, ddaD and ddaE) and at a low level in the class IV md neurons (ddaC, v'ada and vdaB) (Grueber et al., 2003; W. Grueber, personal observations). Its accumulation pattern in the vtd neurons has not been investigated. |
|
It accumulates in the class IV md neurons (vmd1a, vmd4a and ddaC) (Grueber et al., 2003). Same pattern as Collier, B6-2-25 and Pickpocket. Its accumulation pattern in the vtd neurons has not been investigated. |
|
It accumulates in all the md neurons (Gao et al., 1999) but not in es neurons (Brenman et al., 2001). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004).
|
|
|
|
|
|
IG1-1
|
|
IG1-2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| It accumulates in the ddaE and vpda neurons (a subset of class I neurons) (Sugimura et al., 2003). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004). |
|
It accumulates in all the md neurons but not in ch or es neurons (Sugimura et al., 2003). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| NP1161
|
|
NP2225
|
|
NP7028
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| It accumulates in the class IV md neurons (vmd1a, vmd4a and ddaC) (Sugimura et al., 2004). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004). |
|
It accumulates in the class I md neurons (ddaD, ddaE and vpda) (Sugimura et al., 2003). This P-element is inserted into the abrupt gene (Sugimura et al., 2004). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004). |
|
It accumulates in the class IV md neurons (vmd1a, vmd4a and ddaC) (Sugimura et al., 2003). This Gal4 line starts driving transgene expression at stage 15 (Sugimura et al., 2004). |
|
|
|
|
|
ppk1.9GAL4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The
ppk1.9GAL4 transgene was constructed using a 1.9-kb DNA fragment
located just upstream of the predicted ppk translation start site.
ppk1.9GAL4 is expressed in the class IV md neurons vmd1a, vmd4a and ddaC (Ainsley et al., 2003).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
References
Ainsley JA, Pettus JM, Bosenko D, Gerstein
CE, Zinkevich N, Anderson MG, Adams CM, Welsh MJ, Johnson WA. 2003.
Enhanced locomotion caused by loss of the Drosophila DEG/ENaC protein
Pickpocket1. Curr Biol. 13, pp. 1557-63. Medline
Brenman JE, Gao FB, Jan LY, Jan YN. 2001. Sequoia, a tramtrack-related zinc finger protein, functions as a
pan-neural regulator for dendrite and axon morphogenesis in Drosophila. Dev Cell. 1(5):667-77. Medline
Gao FB, Brenman JE, Jan LY, Jan YN. 1999. Genes
regulating dendritic outgrowth, branching, and routing in Drosophila.
Genes Dev. 13, pp. 2549-61. Medline
Grueber, W. B., Jan, L. Y. and Jan, Y. N.
2003. Different levels of the homeodomain protein cut regulate distinct
dendrite branching patterns of Drosophila multidendritic neurons. Cell
112, pp. 805-18. Medline
Hewes RS, Park D, Gauthier SA, Schaefer AM, Taghert PH. 2003. The bHLH
protein Dimmed controls neuroendocrine cell differentiation in
Drosophila. Development 130(9):1771-81. Medline
Long, A.R., Yang, M., Kaiser, K., Shepherd, D.
1998. Isolation and characterisation of smallminded, a Drosophila gene
encoding a new member of the Cdc48p/VCP subfamily of AAA proteins. Gene
208, 191–199. Medline
Shepherd D, Smith SA. 1996. Central
projections of persistent larval sensory neurons prefigure adult
sensory pathways in the CNS of Drosophila. Development 122, pp. 2375-84. Medline
Sugimura, K., Yamamoto, M., Niwa, R., Satoh, D., Goto, S., Taniguchi,
M., Hayashi, S. and Uemura T. 2003. Distinct developmental modes and
lesion-induced reactions of dendrites of two classes of Drosophila
sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 23, pp. 3752-60. Medline
Sugimura, K., Satoh, D., Estes, P., Crews, S.
and Uemura, T. 2004. Development of Morphological Diversity of
Dendrites in Drosophila by the BTB-Zinc Finger Protein Abrupt. Neuron 43, pp. 809-22. Medline
Williams DW, Truman JW. Cellular mechanisms
of dendrite pruning in Drosophila: insights from in vivo time-lapse of
remodeling dendritic arborizing sensory neurons.2005. Development 132, pp. 3631-42. Medline
Comments and additions are welcome at: Virginie.Orgogozo snv.jussieu.fr