Array operations.
val length : ('a, 'b) array -> 'b int

Return the length (number of elements) of the given array.
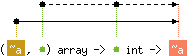
val get : ('a, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'c
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
Array.get a n returns the element number n of array a.
The first element has number 0.
The last element has number Array.length a - 1.Terminate the program if
n is outside the range
0 to (Array.length a - 1).
You can also write a.(n) instead of Array.get a n.
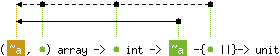
val set : ('a, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'a -{'b ||}-> unit
with 'b < level('a)
with 'b < level('a)
Array.set a n x modifies array a in place, replacing
element number n with x.Terminate the program if
n is outside the range
0 to Array.length a - 1.
You can also write a.(n) <- x instead of Array.set a n x.
val make : 'a int -> 'b -> ('b, 'a) array
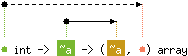
Array.make n x returns a fresh array of length n,
initialized with x.
All the elements of this new array are initially
physically equal to x (in the sense of the == predicate).
Consequently, if x is mutable, it is shared among all elements
of the array, and modifying x through one of the array entries
will modify all other entries at the same time.Terminate the program if
n < 0 or n > Sys.max_array_length.
If the value of x is a floating-point number, then the maximum
size is divided by 2.
val create : 'a int -> 'b -> ('b, 'a) array
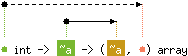
Deprecated.
Array.create is an alias for Array.make.
val init : 'a int ->
('a int -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e) -{'d | 'c |}-> ('e, 'a) array
with 'a, content('c), 'd < 'b
and 'a, content('c), 'd < level('e)
('a int -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e) -{'d | 'c |}-> ('e, 'a) array
with 'a, content('c), 'd < 'b
and 'a, content('c), 'd < level('e)
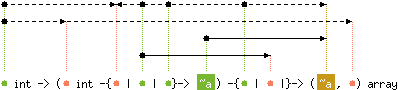
Array.init n f returns a fresh array of length n,
with element number i initialized to the result of f i.
In other terms, Array.init n f tabulates the results of f
applied to the integers 0 to n-1.
val make_matrix : 'a int ->
'b int -> 'c -{'b ||}-> (('c, 'b) array, 'a) array
with 'a < 'b
'b int -> 'c -{'b ||}-> (('c, 'b) array, 'a) array
with 'a < 'b
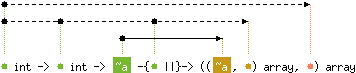
Array.make_matrix dimx dimy e returns a two-dimensional array
(an array of arrays) with first dimension dimx and
second dimension dimy. All the elements of this new matrix
are initially physically equal to e.
The element (x,y) of a matrix m is accessed
with the notation m.(x).(y).Terminate the program if
dimx or dimy is less than 1 or
greater than Sys.max_array_length.
If the value of e is a floating-point number, then the maximum
size is only Sys.max_array_length / 2.
val create_matrix : 'a int ->
'b int -> 'c -{'b ||}-> (('c, 'b) array, 'a) array
with 'a < 'b
'b int -> 'c -{'b ||}-> (('c, 'b) array, 'a) array
with 'a < 'b

Deprecated.
Array.create_matrix is an alias for Array.make_matrix.
val append : ('a, 'b) array -> ('c, 'b) array -> ('d, 'b) array
with 'a, 'c < 'd
with 'a, 'c < 'd
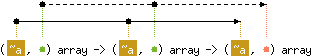
Array.append v1 v2 returns a fresh array containing the
concatenation of the arrays v1 and v2.
val concat : (('a, 'b) array, 'b) list -> ('c, 'b) array
with 'a < 'c
with 'a < 'c
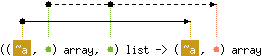
Same as
Array.append, but concatenates a list of arrays.
val sub : ('a, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'b int -> ('c, 'b) array
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)

Array.sub a start len returns a fresh array of length len,
containing the elements number start to start + len - 1
of array a.Terminate the program if
start and len do not
designate a valid subarray of a; that is, if
start < 0, or len < 0, or start + len > Array.length a.
val copy : ('a, 'b) array -> ('c, 'b) array
with 'a < 'c
with 'a < 'c
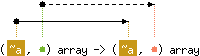
Array.copy a returns a copy of a, that is, a fresh array
containing the same elements as a.
val fill : ('a, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'b int -> 'a -{'b ||}-> unit
with 'b < level('a)
with 'b < level('a)
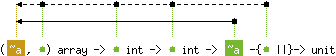
Array.fill a ofs len x modifies the array a in place,
storing x in elements number ofs to ofs + len - 1.Terminate the program if
ofs and len do not
designate a valid subarray of a.
val blit : ('a, 'b) array ->
'b int -> ('c, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'b int -{'b ||}-> unit
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
'b int -> ('c, 'b) array -> 'b int -> 'b int -{'b ||}-> unit
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
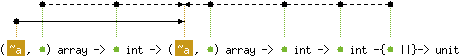
Array.blit v1 o1 v2 o2 len copies len elements
from array v1, starting at element number o1, to array v2,
starting at element number o2. It works correctly even if
v1 and v2 are the same array, and the source and
destination chunks overlap.Terminate the program if
o1 and len do not
designate a valid subarray of v1, or if o2 and len do not
designate a valid subarray of v2.
val to_list : ('a, 'b) array -> ('c, 'b) list
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
with 'a < 'c
and 'b < level('c)
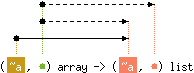
Array.to_list a returns the list of all the elements of a.
val of_list : ('a, 'b) list -{'c ||}-> ('a, 'b) array
with 'b, 'c < level('a)
with 'b, 'c < level('a)

Array.of_list l returns a fresh array containing the elements
of l.
val iter : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'b}-> 'd) -> ('e, 'f) array -{'b | 'c |}-> unit
with 'e < 'a
and 'f < level('a), 'b
and content('c) < 'b
with 'e < 'a
and 'f < level('a), 'b
and content('c) < 'b
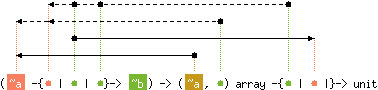
Array.iter f a applies function f in turn to all
the elements of a. It is equivalent to
f a.(0); f a.(1); ...; f a.(Array.length a - 1); ().
val map : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e) ->
('f, 'g) array -{'d | 'c |}-> ('e, 'g) array
with 'f < 'a
and 'g < level('a), 'b, level('e)
and 'd < 'b, level('e)
and content('c) < 'b, level('e)
('f, 'g) array -{'d | 'c |}-> ('e, 'g) array
with 'f < 'a
and 'g < level('a), 'b, level('e)
and 'd < 'b, level('e)
and content('c) < 'b, level('e)
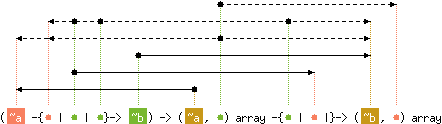
Array.map f a applies function f to all the elements of a,
and builds an array with the results returned by f:
[| f a.(0); f a.(1); ...; f a.(Array.length a - 1) |].
val iteri : ('a int -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'f}-> 'g) ->
('h, 'a) array -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with 'd < 'b, 'f
and 'a < 'b, level('e), 'f
and content('c) < 'b, 'f
and 'h < 'e
('h, 'a) array -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with 'd < 'b, 'f
and 'a < 'b, level('e), 'f
and content('c) < 'b, 'f
and 'h < 'e
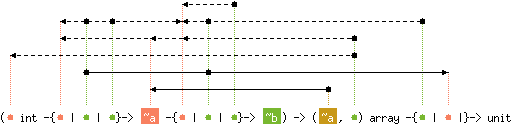
Same as
Array.iter, but the
function is applied to the index of the element as first argument,
and the element itself as second argument.
val mapi : ('a int -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'h) ->
('i, 'a) array -{'d | 'c |}-> ('h, 'a) array
with 'd < 'b, 'f, level('h)
and 'g < 'f, level('h)
and 'a < 'b, level('e), 'f, level('h)
and content('c) < 'b, 'f, level('h)
and 'i < 'e
('i, 'a) array -{'d | 'c |}-> ('h, 'a) array
with 'd < 'b, 'f, level('h)
and 'g < 'f, level('h)
and 'a < 'b, level('e), 'f, level('h)
and content('c) < 'b, 'f, level('h)
and 'i < 'e
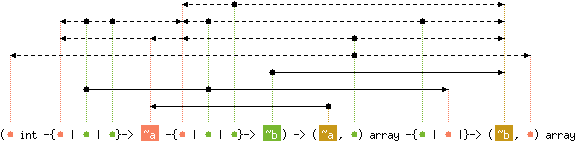
Same as
Array.map, but the
function is applied to the index of the element as first argument,
and the element itself as second argument.
val fold_left : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'a) ->
'a -> ('h, 'i) array -{'d | 'c |}-> 'a
with 'i < level('a), 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'd < level('a), 'b, 'f
and 'g < level('a), 'f
and content('c) < level('a), 'b, 'f
and 'h < 'e
'a -> ('h, 'i) array -{'d | 'c |}-> 'a
with 'i < level('a), 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'd < level('a), 'b, 'f
and 'g < level('a), 'f
and content('c) < level('a), 'b, 'f
and 'h < 'e
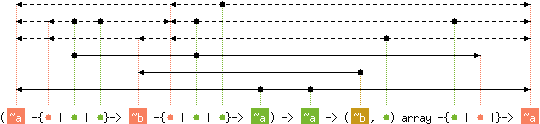
Array.fold_left f x a computes
f (... (f (f x a.(0)) a.(1)) ...) a.(n-1),
where n is the length of the array a.
val fold_right : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'e) ->
('h, 'i) array -> 'e -{'d | 'c |}-> 'e
with 'h < 'a
and 'i < level('a), 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'd < 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'g < level('e), 'f
and content('c) < 'b, level('e), 'f
('h, 'i) array -> 'e -{'d | 'c |}-> 'e
with 'h < 'a
and 'i < level('a), 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'd < 'b, level('e), 'f
and 'g < level('e), 'f
and content('c) < 'b, level('e), 'f
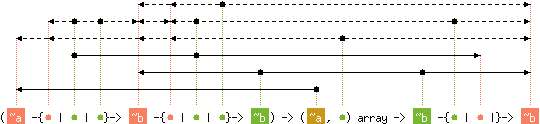
Array.fold_right f a x computes
f a.(0) (f a.(1) ( ... (f a.(n-1) x) ...)),
where n is the length of the array a.