MENTA
Accessible Quantifiers of Multipartite Entanglement in Atomic Systems
Context
Bell’s theorem [1] establishes that the correlations predicted by quantum mechanics for entangled systems cannot be explained by any local realistic theory. Experimental violations of Bell inequalities have been demonstrated convincingly with photons [2-4] and, more recently, with massive particles using internal degrees of freedom such as spin [5]. However, tests of nonlocality involving massive particles entangled in their motional degrees of freedom are still absent [6].
In this project, we propose to set up an atomic interferometer [7] and a bright source of momentum entangled particles [8] to conduct a Bell test.
Results
-
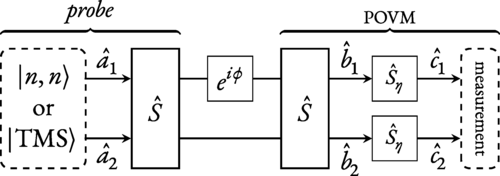
Sub-shot-noise interferometry with two-mode quantum states
We discuss the optimization of quantum enhanced interferometers when taking into account losses.
-

Pulse shaping for atomic Bragg diffraction
We have developed a new four-mode atomic interferometer that we propose to use in a Bell test.
-
Probing entanglement of two-mode bosonic Gaussian states
In this theoretical work, we show how to quantify entanglement of some two-mode bosonic Gaussian states relying on their full probability distribution i.e. by only counting particles.
Bibliography
[1] J. S. Bell, On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen paradox, Physics Physique Fizika 1, 195 (1964)
[2] A. Aspect, P. Grangier, and G. Roger, Experimental Tests of Realistic Local Theories via Bell’s Theorem, Phys. Rev. Lett. 47, 460 (1981).
[3] A. Aspect, J. Dalibard, and G. Roger, Experimental Test of Bell’s Inequalities Using Time- Varying Analyzers, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1804 (1982).
[4] J. G. Rarity and P. R. Tapster, Experimental violation of Bell’s inequality based on phase and momentum, Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 2495 (1990).
[5] D. K. Shin, B. M. Henson, S. S. Hodgman, T. Wasak, J. Chwedeńczuk, and A. G. Truscott, Bell correlations between spatially separated pairs of atoms, Nat Commun 10, 4447 (2019).
[6] Lewis-Swan, R. J. & Kheruntsyan, K. V., Proposal for a motional-state Bell inequality test with ultracold atoms, Phys. Rev. A 91, 052114 (2014)
[7] M. Bonneau, J. Ruaudel, R. Lopes, J.-C. Jaskula, A. Aspect, D. Boiron, and C. I. Westbrook, Tunable source of correlated atom beams, Phys. Rev. A 87, 061603 (2013).
[8] P. Dussarrat, M. Perrier, A. Imanaliev, R. Lopes, A. Aspect, M. Cheneau, D. Boiron, and C. I. Westbrook, Two-Particle Four-Mode Interferometer for Atoms, Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 173202 (2017).